Overview.
A small parasite that infects the red blood cells is Babesia. Babesia Infection is referred to as babesiosis. Typically, the parasitic infection is spread by a tick bite.
Like Lyme disease, babesiosis also happens at the same time. With the Babesia parasite, the tick containing the Lyme bacteria may also be infected.
Microscopic parasites that infect red blood cells and are transmitted by some ticks are the cause of babesiosis.
Tick-borne transmission is most prominent in various areas and seasons in the United States: it occurs primarily in parts of the Northeast and upper Midwest and typically peaks during the warm months.
Although there are no signs for those people who are afflicted with Babesia, appropriate care is required for those who do so. When simple precautions are taken to minimise tick infection, babesiosis is preventable.
Babesia microti is spread, usually by the nymph stage of the tick, which is around the size of a poppy seed, by the sting of infected Ixodes scapularis ticks. On the face of a penny, an Ixodes scapularis nymph is shown.
What is Babesiosis?
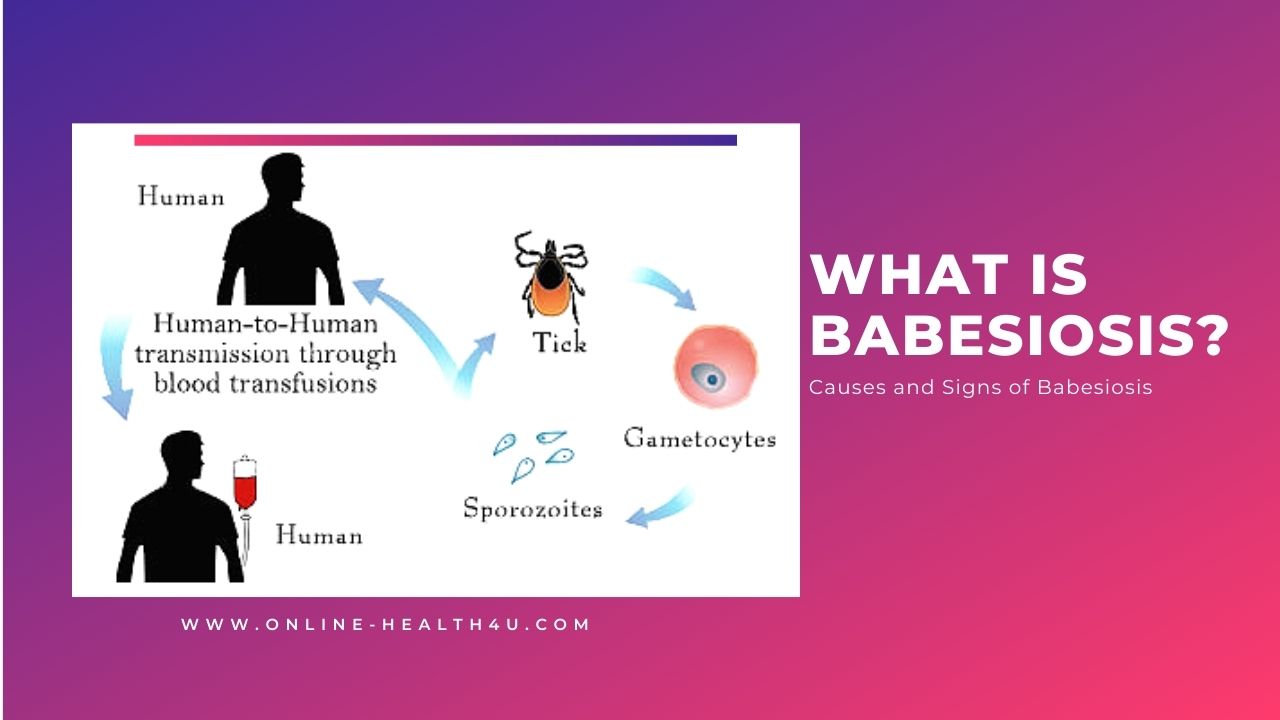
Babesiosis is a condition caused by red blood cells being infected by microscopic parasites. In mammals, several distinct species (types) of Babesia parasites have been found, only a handful of which have been found in humans.
The predominant species that have been found in people in the United States is Babesia microtia, which typically infects white-footed mice and other small rodents. Occasional events have been detected caused by other Babesia species.
Babesiosis is an infectious disease caused by parasites that break open red blood cells and attack them. In the United States, babesiosis is caused by Babesia microti, especially along the northeastern seaboard. The most popular (left panels) are the ring type, while tetrads are rare (right panels).
Babesia microti is borne by white-footed rodents, and the deer tick is passed from one rodent to another. Sadly, deer ticks feed on humans, thereby spreading the parasite.
Babesiosis may be life-threatening in comparison to Lyme disease, its fellow traveler. The infection also can be acquired through the transfusion of contaminated blood products.
Complications and Signs.
The severity of the babesiosis symptoms can vary. You may not have any symptoms, or you may have mild flu-like symptoms at all. Significant, life-threatening complications can happen in some situations.
High fever, chills, muscle or joint aches, and exhaustion most commonly begin with a Babesia infection.
Symptoms that are less frequent include:
- Headache that is serious
- Pressure in the belly
- Nausea and sickness
- Bruising on the surface
- Yellowing in your eyes and skin
- Changes in mood
You can experience chest or hip pain, shortness of breath, and drenching sweats with the infection developing.
You may be sick with Babesia and have no symptoms at all. Relapsing high fever is a symptom of undiagnosed babesiosis at times.
These can involve complications:
- Very low level of blood pressure
- Troubles in the liver
- Red blood cell degradation, known as hemolytic anemia
- Kidney breakdown
- Heart insufficiency
There will be no symptoms for most persons in the US who become afflicted with babesiosis, but some may have tiredness, fever, malaise, jaundice, and anemia.
Symptoms will last from a few days to a few months, usually appearing 1-4 weeks after infection. The disorder usually goes away on its own in asymptomatic persons.
Symptoms of babesiosis usually begin one to six weeks after inoculation in immunocompetent patients and are non-specific. Intermittent fevers associated with weakness and malaise, headache, chills, and myalgia are common early symptoms.
There may also be fatigue, vomiting, a diminished appetite, and depression. Any patients have swollen livers or spleens that may improve. The normal phase of the disease continues for weeks to several months, but some people take much longer to heal completely.

Lyme disease or anaplasmosis co-infection may worsen the clinical appearance and predispose the patient to more serious illness.
Elderly people, asplenic patients, patients with HIV or malignancies, and patients taking immunosuppressive medications are at the highest risk for serious babesiosis.
The disease path is longer in these communities and the fatality risk, even with adequate antibabesial treatment, is 20 percent in the neighborhood.
Acute respiratory failure is the most frequent extreme complication of babesiosis, but cardiac failure, liver, and renal failure, disseminated intravascular coagulation, and coma are all well-recognized significant symptoms of babesiosis.
Causes.
Babesiosis is caused by microorganisms from the genus Babesia that are single-celled (protozoa). Parasites that attack red blood cells are these micro-organisms (erythrocytes).
Babesia has more than 100 species. In certain cases, Babesia microtia and Babesia divergens are the two species of Babesia that cause sickness in humans (pathogenic). Depending on the precise geographic location, the species concerned vary.
In the northeastern United States, the main cause of babesiosis is infection with B. Yeah. Microti. A new Babesia parasite, called WA-1, is suspected to be responsible for the disease in California and Washington. Inside Europe, B. Divergenes, B. Bovis are usually liable for babesiosis.
Such babesia protozoa as B. Microti is spread by the saliva of infected ticks on humans. The ticks function as "vectors," the term for any organism that is infected with a certain disease agent (e.g. bacterium or virus) and later transmits it to another organism, which may then become infected.
The most common vector that transmits Babesiosis is the deer tick (Ixodes dammini or scapularis). Babesiosis can be spread after a blood transfusion of blood that is infected with the microorganism in very rare cases.
Babesiosis is caused by infection with a malaria-like parasite of the genus Babesia. The Babesia parasite can also be called Natalia.
The parasite grows and reproduces inside the red blood cells of the infected person or animal, often causing intense pain due to the rupture of red blood cells.
There are more than 100 species of the Babesia parasite. In the United States, Babesia microti is the most commonTrusted Source strain to infect humans, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)Trusted Source. Other strains can infect:
- Cattle
- Horses
- Sheep
- Pigs
- Goats
- Dogs
How is babesiosis transmitted?
The sting of an infected black-legged (deer) tick spreads babesiosis. The longer a tick stays attached and eats, the greater the probability that the infection can spread. Generally, the tick must be attached to the human for at least 24-36 hours before the germ can spread.
The germs that cause Lyme disease and human granulocytic anaplasmosis can also be borne by black-legged ticks in Massachusetts. These ticks are able to disperse more than one form of germ in a single bite.
When can I get babesiosis?
During any time of year, babesiosis can occur. Infected black-legged ticks transmit the infection that causes babesiosis. During the warm weather months between May and July, young ticks (nymphs) are the most involved.
Adult ticks are more aggressive during the fall and spring, but at any time when winter temperatures are above freezing, they can even be out looking for a host.
Diagnosis.
Babesiosis diagnosis is based on the signs and symptoms of the patient, a history of potential exposure, and adequate laboratory tests. For timely diagnosis and treatment, early identification of symptoms is critical.
Ask the healthcare provider right away if you suspect you have babesiosis.
People who have removed an attached tick often ask whether they should have tick-borne illnesses screened for it. Though this testing is proposed by some laboratories, ISDH does not recommend it.
It does not actually mean that you have been infected if the tick tests positive; if the tick tests negative, it can give a false sense of protection that a certain tick that was infected may have bitten you unknowingly.
Treatment.

Babesia is a parasite that alone will not respond to antibiotics. Antiparasitic medications, such as those used for malaria, are required for treatment. For the treatment in most mild to severe conditions, Atovaquone +azithromycin is used and is normally taken for 7 to 10 days. Clindamycin and quinine is an alternative regimen.
Extreme disease management normally consists of intravenous administration of azithromycin plus oral intravenous administration of atovaquone or clindamycin plus oral quinine. Additional supportive steps such as blood transfusions can be taken for serious illness.
During recovery, it is possible for relapses to happen. They must be re-treated if you have signed again. Few patients, such as those with compromised immune systems, may initially need to be monitored for longer to clear up the infection.



2 Comments
Our GTA 5 Drudge and Cheats online is completely available and anyone can have recourse to it. You do not need to leftover your actual currency anymore while buying the Practical GTA 5 Greenbacks or Position which you against to secure from ROCKSTAR Unflinching or from any third party and may many times you got scammed on these Well-heeled and RP seller. http://www.googlep10.com
ReplyDeleteThis comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDelete